Did you know that the average American consumes a mere 15 grams of protein per day, far below the recommended intake? This crucial macronutrient plays a vital role in your overall health and well-being, serving as the building block for your muscles, bones, and tissues. In this article, we’ll dive into the importance of protein, its various functions, recommended protein requirements, and the best protein sources, including plant-based and animal-derived options.
Key Takeaways
- Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a crucial role in your body’s growth, repair, and maintenance.
- Protein benefits include muscle building, weight management, and stronger bones.
- The recommended daily protein intake varies based on factors like age, gender, and activity level.
- Both plant-based and animal-derived protein sources can provide the necessary nutrients.
- Protein deficiency can lead to muscle wasting, weakened immunity, and increased illness risk.
Unveiling the Importance of Protein
Protein is one of the three macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and fats, that your body requires in large quantities to function properly. It is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of your cells, tissues, and organs. Protein plays a crucial role in various bodily processes that are essential for your overall health and well-being.
Protein: A Macronutrient Essential for Life
As one of the key protein benefits, this macronutrient is necessary for the proper growth, repair, and maintenance of your body’s tissues. Protein helps build and maintain your muscles, bones, skin, and other vital structures, making it an indispensable part of your dietary needs.
Roles of Protein in the Human Body
In addition to its structural roles, protein also supports various other important functions in your body, including:
- Enzyme and hormone production: Protein is a key component in the creation of enzymes and hormones that regulate important bodily functions.
- Immune function: Protein supports the proper functioning of your immune system, helping you fight off infections and illnesses.
- Energy production: While not the primary source of energy, protein can be used by your body for fuel if necessary.

Ensuring you consume adequate amounts of high-quality protein sources is crucial for maintaining optimal protein requirements and supporting your overall health and well-being.
Unraveling the Benefits of Adequate Protein Intake
Consuming the right amount of protein can provide you with a wide range of health benefits, including:
Muscle Growth and Maintenance
Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue, which is crucial for maintaining strength and overall physical function. A high protein diet can help you build and maintain lean muscle mass, enhancing your physical performance and reducing the risk of injury.
Weight Management and Satiety
Protein-rich foods tend to be more filling and can help you feel satisfied for longer, which can aid in weight management and prevent overeating. Incorporating protein supplements and other high protein sources into your diet can be beneficial for those seeking to achieve or maintain a healthy weight.
Strong Bones and Injury Prevention
Protein works alongside calcium and other nutrients to support bone health, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Adequate protein intake is essential for maintaining strong, healthy bones, which can help prevent injuries and improve overall mobility and function.

Why You Need Protein: Recommended Intake and Requirements
The protein requirements for your body can vary depending on factors such as your age, gender, and activity level. Generally, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for adults is 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, individuals with certain health conditions, those who are physically active, or those trying to build muscle may need higher amounts of protein to meet their specific needs.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine your protein requirements and ensure you’re consuming the right amount to support your overall health and why you need protein. Insufficient protein intake, or protein deficiency, can lead to a range of negative consequences, which we’ll explore in more detail in the next section.
| Age Group | Recommended Protein Intake (g/kg body weight) |
|---|---|
| Children (1-13 years) | 0.85-1.2 |
| Teens (14-18 years) | 0.85-1.2 |
| Adults (19-70 years) | 0.8 |
| Older Adults (over 70 years) | 1.0-1.2 |
| Pregnant Women | 1.1 |
| Breastfeeding Women | 1.3 |
Remember, these are general guidelines, and your protein requirements may vary based on your individual needs and health status. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is the best way to ensure you’re meeting your protein requirements and reaping the full benefits of this essential nutrient.

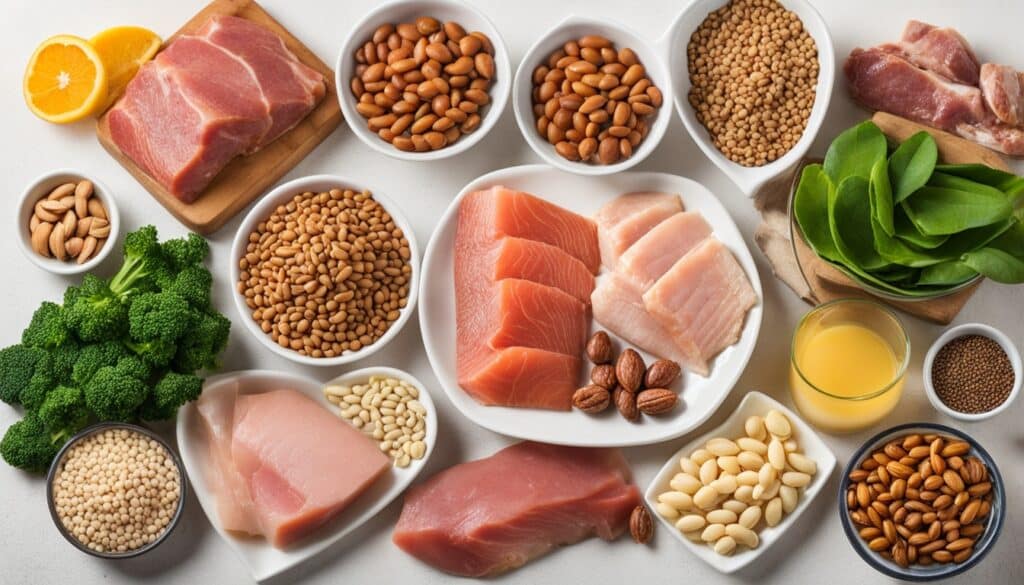
Exploring Protein Sources: Plant-Based and Animal-Derived
Protein can be obtained from a variety of both plant-based and animal-derived sources. Incorporating a balanced mix of these
into your diet can help you meet your daily protein requirements and reap the full benefits of this essential nutrient.
Plant-Based Protein: Legumes, Nuts, and Grains
If you follow a plant-based proteins diet or simply want to increase your intake of plant-based protein, there are numerous options to choose from. Some of the best plant-based protein sources include legumes like beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas, as well as nuts and seeds like almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and hemp seeds. Whole grains, such as quinoa, oats, brown rice, and whole wheat bread, also provide valuable plant-based proteins.
Animal-Derived Protein: Meat, Dairy, and Eggs
For those who consume animal proteins, there are also many excellent sources to consider. Lean meats, poultry, fish, and seafood are all excellent sources of high-quality animal proteins. Dairy products, including milk, yogurt, and cheese, are also rich in animal proteins. Eggs, a versatile and convenient option, are another fantastic animal protein source.
Protein Deficiency: Signs, Symptoms, and Risks
While protein deficiency is relatively uncommon in developed countries, it can occur in certain populations, such as those with limited access to food, those following restrictive diets, or those with certain medical conditions. Symptoms of protein deficiency can include:
Muscle Wasting and Weakness
Without adequate protein, your body may break down muscle tissue for energy, leading to a loss of muscle mass and strength. This can significantly impact your physical performance and overall well-being.
Impaired Immunity and Increased Illness Risk
Protein plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of your immune system. A deficiency can make you more susceptible to infections and illnesses, increasing your risk of falling ill and compromising your overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, protein is a vital nutrient that your body needs for a wide range of essential functions, from building and repairing tissues to supporting immune health and energy production. By ensuring you consume enough high-quality protein from a variety of sources, you can enjoy the numerous benefits it provides and maintain optimal overall health and well-being.
Whether you’re looking to build muscle, manage your weight, or simply support your overall bodily functions, incorporating the right amount of protein into your diet is crucial. By understanding the importance of protein and exploring the wide range of protein sources available, you can take the necessary steps to meet your unique protein requirements and unlock the full potential of this essential macronutrient.
Remember, your body’s protein needs may vary depending on your age, activity level, and overall health. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the optimal protein intake for your individual needs. With the right protein strategy in place, you can embark on a journey towards improved physical and mental well-being, empowered by the power of this fundamental nutrient.